Architectural English
- ebalabanfaruk

- Sep 20, 2024
- 9 min read
Updated: Jan 28
HEADLINES
Understanding Architectural Terminology: Key Concepts for Advanced Learners
The Language of Architecture: Essential Vocabulary and Phrases
From Blueprints to Buildings: Navigating Architectural English
Architectural Structures: Exploring Terminology and Descriptions
Mastering Technical Terms in Architecture: A Guide for English Learners
Architectural Styles and Their Vocabulary: From Gothic to Modernism
Describing Buildings: How to Talk About Architecture in English
The Role of Form and Function in Architecture: A Terminology Guide
Building Materials and Construction Terms: Vocabulary for Architects
Architectural Design Processes: Understanding the Language of Planning and Development
1. Understanding Architectural Terminology: Key Concepts for Advanced Learners
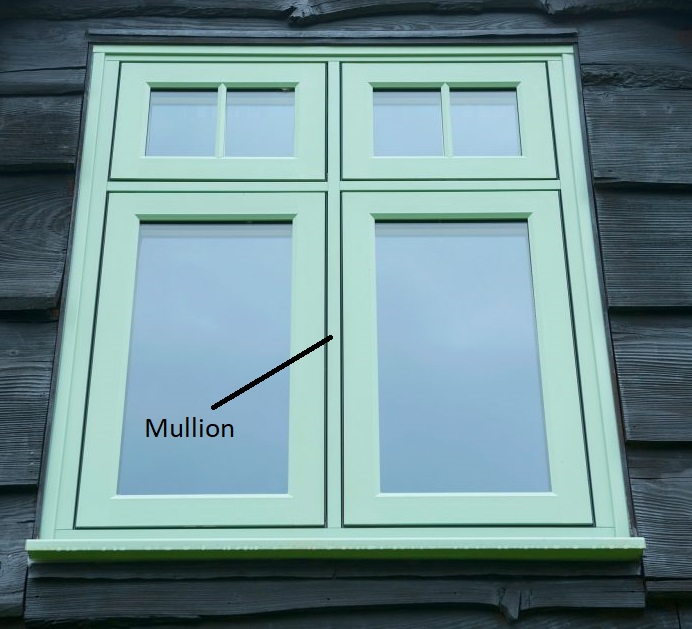
Architectural terminology is essential for anyone involved in design, construction, or even discussing buildings professionally. For advanced English learners, mastering these terms not only builds language proficiency but also opens doors to engaging in global architectural discourse. Key concepts include "load-bearing structures", which refer to elements that support the weight of the building, and "cantilevers", a projecting beam or structure anchored at only one end. Learning terms like "fenestration" (the design and placement of windows) or "masonry" (building with bricks, stones, or concrete blocks) allows learners to describe intricate details of buildings. Mastering the names of architectural movements like "Gothic," "Baroque," or "Brutalism" will further help students contextualize buildings within their historical and cultural frames. This knowledge is foundational for understanding architectural plans, specifications, and professional conversations about design.
2. The Language of Architecture: Essential Vocabulary and Phrases
The world of architecture is rich with unique vocabulary that spans both technical and descriptive language. For example, terms such as "façade" describe the exterior face of a building, usually the front, while "atrium" refers to an open central space inside a building. These words enable architects, engineers, and designers to communicate the function and form of a structure clearly. Phrases like "integrated design" highlight the holistic approach to building where architecture, structure, and systems are developed concurrently. Learners should also familiarize themselves with "sustainable architecture" terms, such as "green roofs", "LEED certification", and "passive solar design", which are increasingly important in modern construction. Understanding these key phrases and vocabulary sets a foundation for deeper discussions on building concepts and designs.
3. From Blueprints to Buildings: Navigating Architectural English
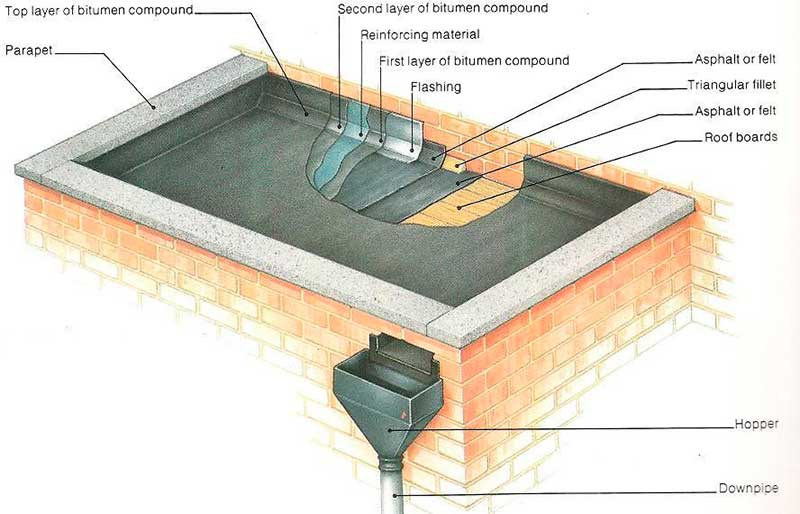
Architectural blueprints serve as the starting point for any construction project, and understanding the language behind them is critical. Terms like "elevations" refer to drawings that show the building’s vertical plane, while "plans" focus on the horizontal layout of a space. "Sections" give a view of the building as if cut through to show the internal arrangement. Additionally, words like "scale" (the proportion between the drawing and the actual building) and "legend" (the explanation of symbols used in the drawing) are crucial to interpreting and discussing blueprints accurately. Advanced learners must also familiarize themselves with terms like "cross bracing" (supportive diagonal structural members) or "floor plate" (the layout of a building’s floor). Gaining mastery over these terms helps ensure clear communication with architects, engineers, and contractors.
4. Architectural Structures: Exploring Terminology and Descriptions
Architectural structures are diverse, and each type of structure comes with its own specific terminology. Whether discussing a "truss" (a framework, typically consisting of rafters and posts) or "arches", which are curved structures used to support weight, these terms are essential for describing the composition of buildings. Advanced learners should also be aware of modern structures like "geodesic domes", which distribute stress across the surface, or "tensile structures" that use tension to support the roof. Structural components like "columns" (vertical structural elements) and "beams" (horizontal supports) are essential vocabulary for anyone involved in discussing building construction. Understanding the differences between "reinforced concrete", "steel frames", and "wooden beams" enables students to compare and contrast different building methodologies with precision and clarity.
5. Mastering Technical Terms in Architecture: A Guide for English Learners
Technical language in architecture extends beyond simple vocabulary and into specialized jargon used by professionals. For instance, understanding the term "programming" in architecture refers to the process of determining the spatial needs and functions of a building, while "site analysis" involves assessing the conditions of the location where a building will be constructed. Mastery of phrases like "urban infill" (developing vacant or underused land within urban areas) or "adaptive reuse" (repurposing old buildings for new uses) is crucial for advanced learners aiming to excel in architectural discussions. Knowing the difference between "retrofitting" (adding new technology or features to old buildings) and "renovating" (restoring a building to its original state) allows for precise communication in professional settings. Technical architectural language is a powerful tool for participating in more detailed and complex discussions about design and construction.
6. Architectural Styles and Their Vocabulary: From Gothic to
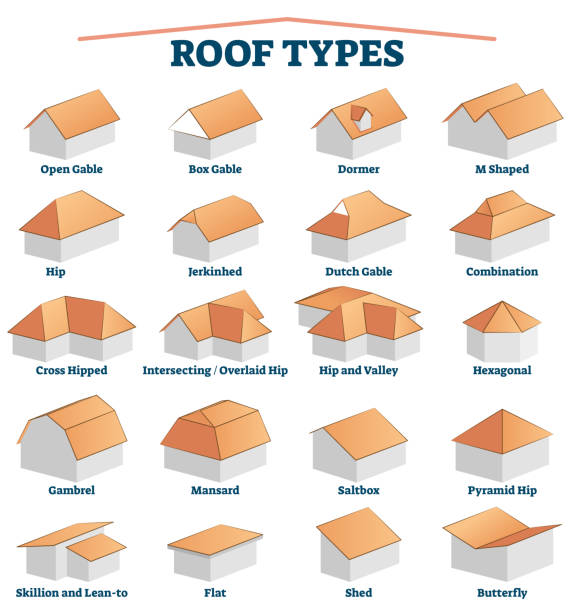
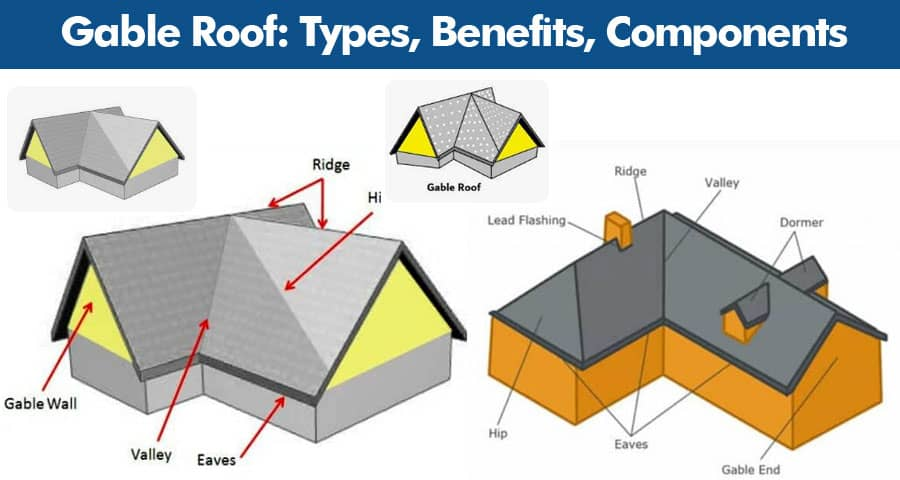
Understanding architectural styles is not just about knowing how a building looks; it's also about understanding the vocabulary associated with each style. "Gothic architecture", for instance, is characterized by features such as "pointed arches", "ribbed vaults", and "flying buttresses", which allowed for the creation of towering, light-filled cathedrals. Moving into "Modernism", we encounter terms like "minimalism", "open floor plans", and "function over form", which emphasize the use of space and materials in a functional way. "Brutalism" employs "raw concrete" and "blocky, fortress-like" shapes, evoking a sense of strength and starkness. Each architectural style has its own vocabulary, and learning these terms helps students place buildings within their historical and stylistic context, allowing for a richer, more detailed discussion of architectural evolution.
7. Describing Buildings: How to Talk About Architecture in English
When discussing buildings in English, learners must go beyond basic adjectives like "big" or "tall" and use precise vocabulary. Describing the "façade" of a building, for example, involves noting its material, symmetry, and decorative elements. Terms like "asymmetry", "proportion", and "ornamentation" are useful for discussing the design choices of a structure. Descriptions can also include whether a building is "monolithic" (appears as one large, unbroken structure) or "articulated" (has distinct parts or sections). When evaluating interior spaces, learners can use terms like "spacious", "intimate", or "modular" to describe the feel and flow of a room. Learning to articulate these ideas fluently in English enables advanced students to engage deeply with architectural discussions.
8. The Role of Form and Function in Architecture: A Terminology Guide
One of the central debates in architecture is the relationship between form (the appearance of a building) and function (how the building is used). "Form follows function", a famous principle of modernist architecture, suggests that a building’s design should primarily reflect its purpose. However, in many architectural styles, form is given more importance, leading to highly decorative or symbolic buildings. Terms like "functionalism" (the idea that buildings should be designed based on their function) and "aesthetic" (the artistic aspect of a building) are key to understanding this concept. Learners must also be familiar with "ergonomics", which refers to designing buildings that accommodate human use comfortably and efficiently. Mastering this terminology provides insight into why buildings are designed the way they are, whether for practicality, beauty, or a blend of both.
9. Building Materials and Construction Terms: Vocabulary for Architects
Understanding the materials used in construction is crucial for anyone involved in architecture. Common materials like "brick", "concrete", "timber", and "steel" each have distinct properties and uses in construction. More advanced learners should familiarize themselves with terms like "prefabricated" (building parts made off-site and assembled on-site), "cladding" (the external covering of a building), and "load-bearing walls" (walls that support the structure above). Sustainable materials like "bamboo" or "rammed earth" are becoming increasingly important in modern architecture, so learners should also be aware of these terms. Knowing the vocabulary related to building materials not only helps in discussing structures but also provides insight into the environmental impact and technological advances in construction.
10. Architectural Design Processes: Understanding the Language of Planning and Development
Architectural design is a complex process that begins with "conceptual design", where the initial idea or vision for a building is developed. From there, architects move to "schematic design", creating rough sketches and layouts of the project. Terms like "renderings" (visual representations of what the final building will look like) and "site plans" (detailed layouts of how a building will sit on the land) are essential vocabulary. During the development phase, architects must also engage with "zoning laws" and "building codes" to ensure their designs meet legal requirements. Words like "budgeting", "sustainability", and "feasibility" are part of the practical aspects of architectural planning. Learning this language allows students to understand the full scope of how a building moves from idea to reality.






















Comments